Preamble
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is a current rage. As the popularity of CBD skyrockets, so does the demand for it. The natural source of CBD is from a plant. Plants take a long time to grow. Plants also require land to grow.
The harvesting and extraction of the molecule from a plant is also a tedious process. All this adds to the cost and limits the supply of natural CBD.
Making synthetic CBD is a relatively cheap process and it can be scaled very rapidly. Industrial production of a synthetic molecule leads itself to the economics of scale.
This paper examines how CBD works in the human body. It also examines how various sources of CBD have been found to affect human health.
Molecules found in nature, especially in plants, are recognized by our DNA and are usually healthy for us. Molecules synthetically created by humans, usually “drugs”, have long lasting negative effects.
This is true for cannabinoids also. CBD from a plant source, such as Hops or Cannabis, do not stress out the human liver. All human studies, including papers published by us, have shown that synthetic cannabinoids, including synthetic CBD, are deleterious to human health.
The headlines are obvious-
“Poisonings in Poland Illustrate Global Challenge of Synthetic Drugs”- https://www.nytimes.com/2015/10/15/world/europe/poisonings-in-poland-illustrate-global-challenge-of-synthetic-drugs.html?searchResultPosition=2
“Tainted Synthetic Marijuana Has Been Sickening People Across the Midwest”- https://www.nytimes.com/2018/04/06/us/chicago-synthetic-marijuana-outbreak.html
“Drug 85 Times as Potent as Marijuana Caused a ‘Zombielike’ State in Brooklyn”- https://www.nytimes.com/2016/12/14/nyregion/zombielike-state-was-caused-by-synthetic-marijuana.html
This article delves further into the human biochemistry of CBD and shows the difference between natural CBD and synthetic CBD within the human body.
Whats An Organic Molecule
Natural CBD is an organic molecule and acts as a “ligand”. Different compounds in nature like odors, pheromones, plant molecules, hormones or neurotransmitters act as ligands and send very specific signals that are interpreted by our body. The strength of these signals is known as its “bioactivity.”
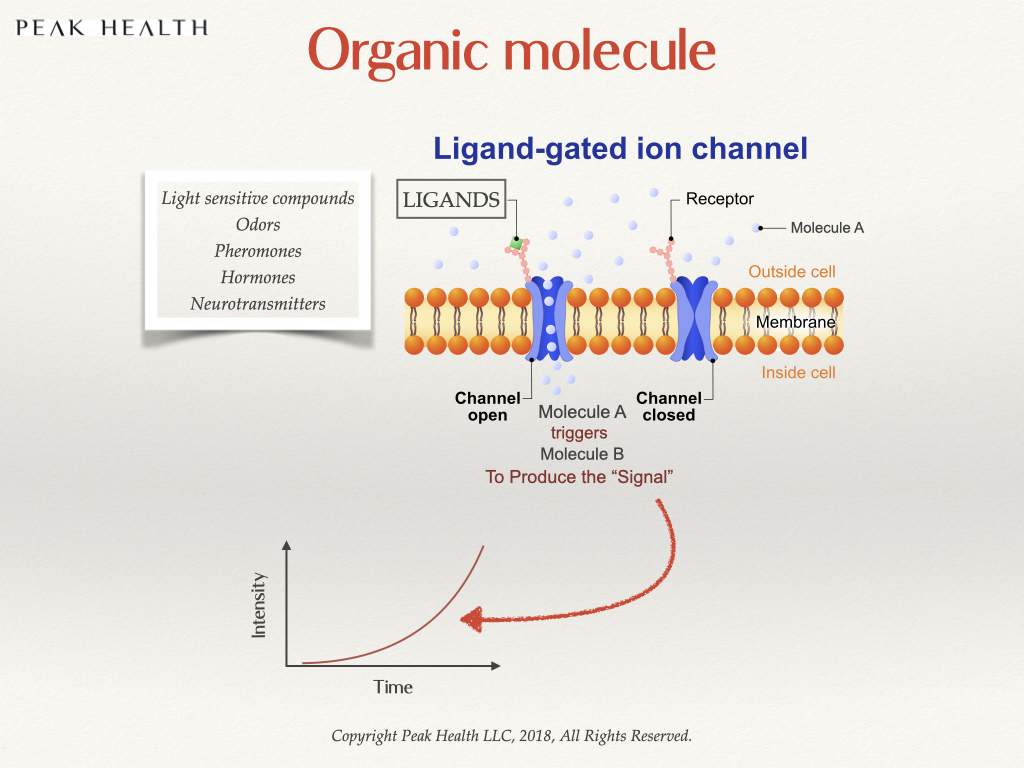
A cayenne pepper contains capsaicin that activates the TRPV1 receptor in our mouth. When cayenne touches our tongue, it sends sensations of “heat” to the brain and it triggers a chain reaction that causes sweating in order to cool ourselves. Some cayenne plants generate less heat and are considered to have low bioactivity. Some cayenne plants are extremely hot and are considered highly bioactive.
What Is A Cannabinoid
A cannabinoid is a molecule that affects the endo-cannabinoid system of the human body.
It does not have to come from a cannabis plant.
β-Caryophyllene, from the patented Kriya® Hops plant, is a potent cannabinoid. Oregeno, cinnamon and black pepper plants are far better sources of β-Caryophyllene than cannabis.
What Is A Cannabinoid Ligand
The pharmaceutical industry understands the effects of “conventional” neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine and GABA, very well and they have developed thousands of drugs that mimic their activity.
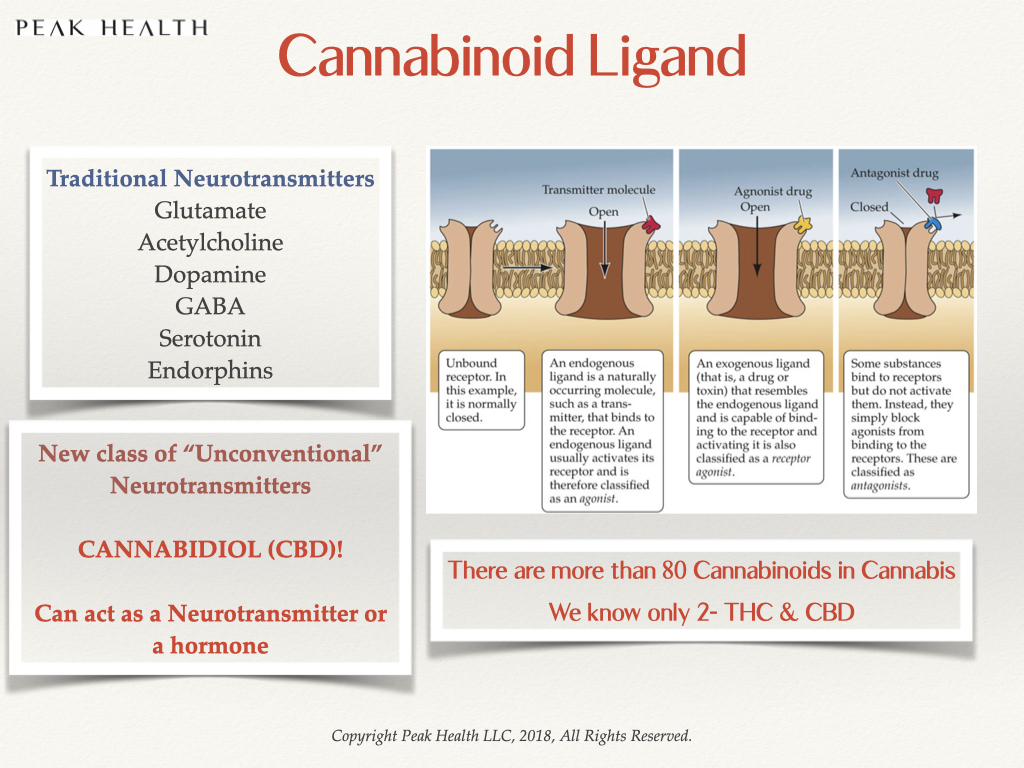
But cannabinoids, as a ligand, are not nearly as well researched, and understood, due to past prohibition laws and social taboos. They act as both, a neurotransmitter and a hormone. Anandamide, one of our body’s internal cannabinoid, stimulates our CB1, CB2 and other lesser receptors.
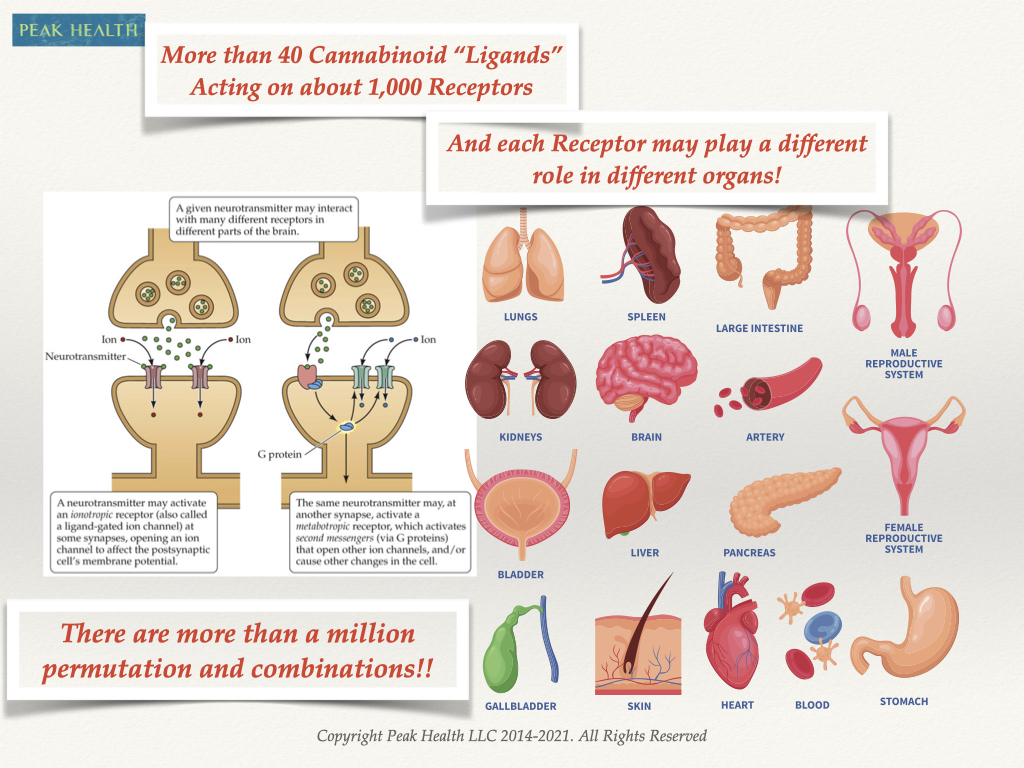
There are more than 40 cannabinoids identified, but only 2 of them, THC and CBD, have been studied in any depth. There are more than 1000 receptor sites – both known and unknown – that these cannabinoids act on. All the permutations and combinations (40+ cannabinoids interacting with 1000s of receptors) make for millions of possible signals that can be sent out by the endo-cannabinoid system. These receptors are in different organs, ranging from the bones to the brain. The same ligand can have a different effect on different organs.
Why Is CBD Important
CBD is a ligand that strongly affects the CB2 and at least 23 other receptors. Crucial organs like our digestive system, heart and blood have a dense collection of CB2 receptors. The CB2 receptor is also very prevalent in the parasympathetic nervous system which affects many things we can’t consciously control such as:
When a liver cell, with CB2 receptors on it, goes rogue and becomes a cancer cell, the number of CB2 receptors on it increases exponentially. This increase in CB2 receptors is an indicator that the cancer cell “knows” it is under fire from the immune system. The increase in the CB2 receptors is an indication that it is critical for the survival of all cells, both normal and malignant.
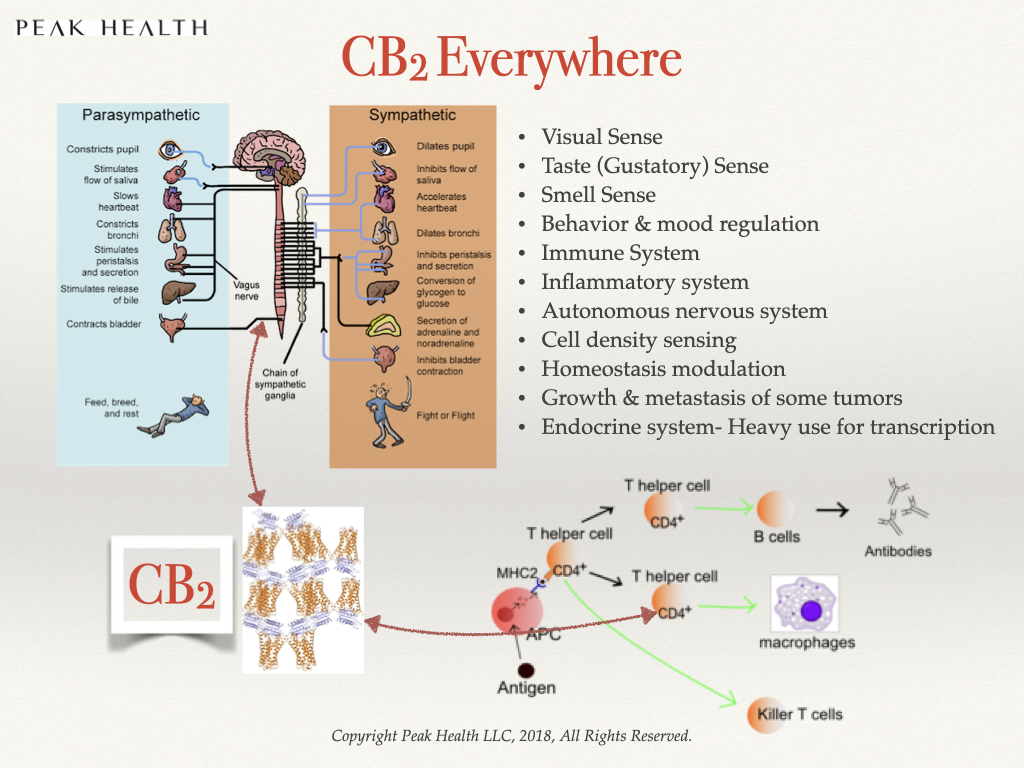
The strong effect of CBD on the CB2 receptor, and the CB2 receptor’s ubiquitous presence in critical pathways of the human body, makes the CBD molecule a potent effector of human health.
Human Inclination To Mess With Nature
Humans and nature are very complementary. But humans have a crazy inclination to mess with nature. And we always screw things up. We mucked up something as simple as margarine. We took cheap natural vegetable oils and tried to simulate more expensive animal fat. All we had to do was bubble hydrogen through vegetable oil. Try as they might, food chemists could never approximate nature.

Since the trans bonds never get cleaved, unwieldy large fat complexes entered the bloodstream. The trans-fat unit has a greater tendency to latch on to the cell wall, greatly contributing to arteriosclerosis. By tinkering with the chemistry of nature’s fats, humans created a serious public health problem. It took the FDA more than 40 years to restrict the use of trans fats.
Humans have never been able to simulate a perfectly natural molecule.
Phytoceuticals vs Synthetic Molecules
Humans evolved from plants and share much of the same DNA. A human being and banana share 60% of the same genetic code. Our body intrinsically recognizes the molecular geometry of the sugars and vitamins in a banana as natural. Our DNA, and our body, is innately tuned to recognize slight imperfections in structures. This is crucial for our survival. Our immune system is perceptive enough to pick up very slight mutations that a virus has undergone and recognize it as the same threat it has encountered before.
Most natural active plant compounds (phytoceuticals) have a long history of human use. They are safe and normally not toxic, and the body doesn’t reject or build tolerance to them.
Natural compounds are made by nature and cannot be patented. The pharmaceutical industry uses plant molecules as models and often develop synthetic drugs “inspired” by nature which can patented and profited from. These drugs almost always have side effects compared to their natural siblings. The body recognizes them as ‘distorted’ and not-quite-legitimate molecules. The body will reject, develop a tolerance, or develop cravings and addiction to these synthetic drugs. This is why all synthetic drugs are required to pass extensive trials and testing.
It’s not advisable to take a pharmaceutical drug for more than three weeks. Three months is usually the absolute maximum recommended duration. Most drugs are recklessly overprescribed in the United States and the headlines indicate that it is a leading scourge in our society today.
Denatured CBD
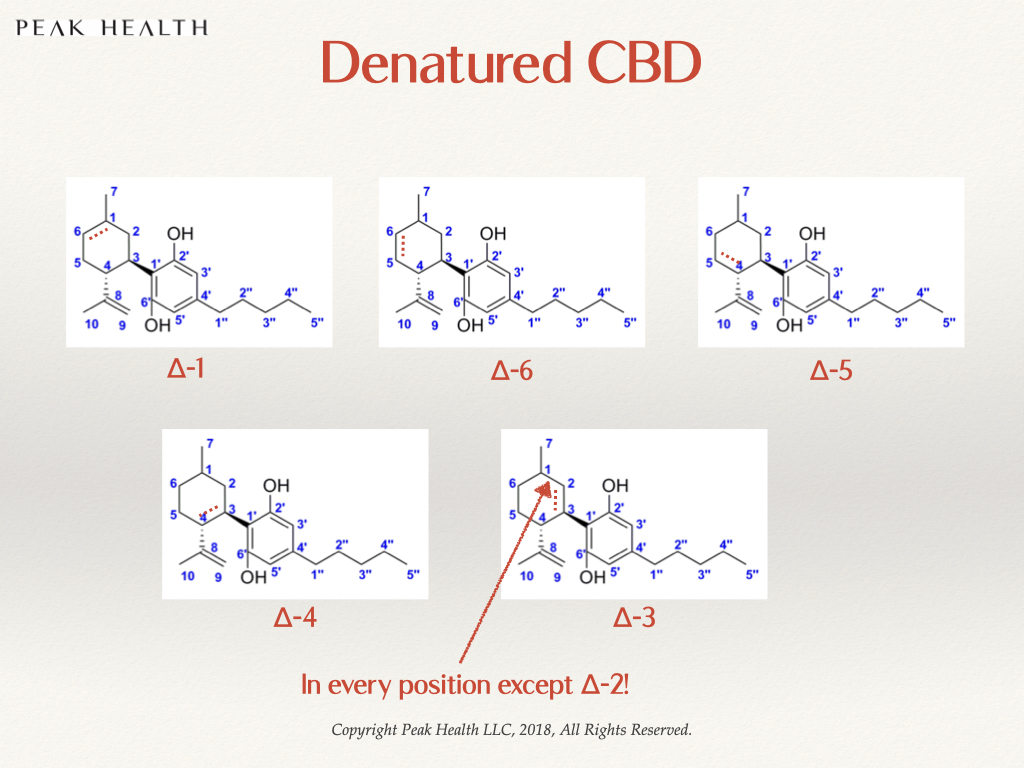
In chemistry, isomers are molecules with the exact same number and types of atoms, but positioned differently. Their electrons are shifted differently in space. The CBD that you get from the natural plant, always has a double bond in the second position (“delta 2 or Δ-2”). When CBD is over processed, denatured or chemically synthesized, different isomeric “types” of CBD are created. The double bond is in the 1st, 3rd, 4th, 5th or 6th (Δ-1, Δ-3, Δ-4, Δ-5, Δ-6) positions. Never in the 2nd.
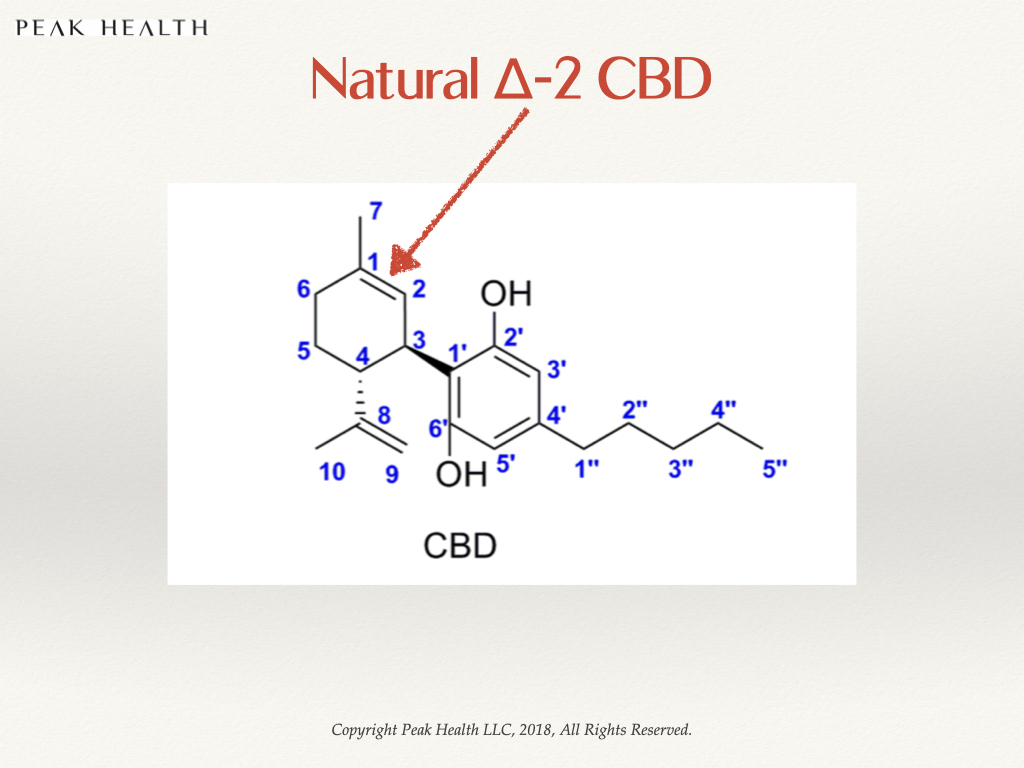
This is very similar to the trans-bond fiasco. The “denatured or synthetic CBD” will be detected as CBD on most spectrographic tests because they have the same molecular weight and shape. But they have inferior effects within the human body. Our DNA and our sensory system “picks up” that something isn’t quite right and responds accordingly.
We have applied for a patent for the anti-Cannabidiol antibody called “Natyam”. The patent application describes the latching mechanism where parts of the antibody attaches to the CBD. The various isomers of CBD, with the shifted bond positions and angles, significantly affects how the antibody molecule latches on to it. Therefore the antibody Natyam is a very sensitive way to measure the functional integrity of the CBD molecule. GC-MS and other lab analytical assays only measure the mass of the molecule, not its functional well being.
Synthetic CBDs
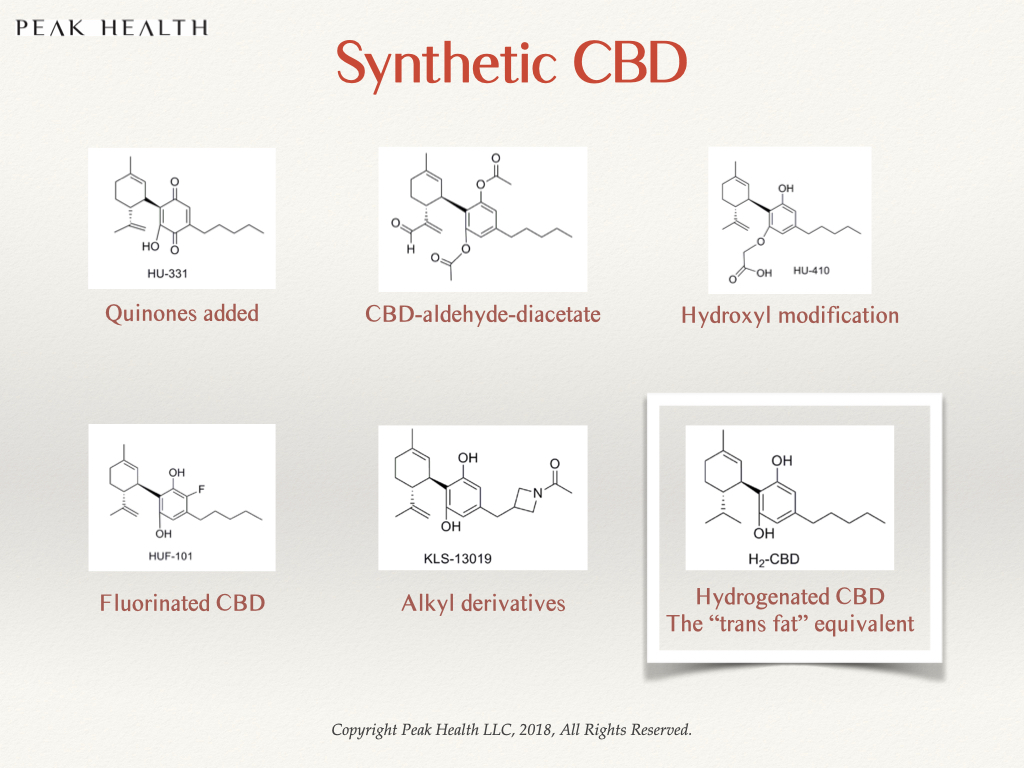
There are many different isomers and synthetic analogues of CBD that are found in literature. They are sometimes found in consumer products on the market. These include:
- CBD-aldehyde-diacetate
- HU-331 – quinones added
- HU-410 – hydroxyl group modification
- HUF-101 – fluorinated CBD
- KLS-13019 – alkyl derivative of CBD
- H2CBD – hydrogenated CBD
Growing hops or hemp as a source of cannabinoids is an expensive, land and labor-intensive undertaking. It takes a lot of space and time to create a substantial supply of natural CBD. Making a synthetic CBD product is often easier and more cost efficient than to extract CBD from a plant. Synthetic CBD analogues can an also be patented and profited from. Therefore there is a lot of interest in manufacturing and distributing synthetic CBD, and synthetic cannabinoids in general.
Effect Of Natural And Synthetic CBD On Humans
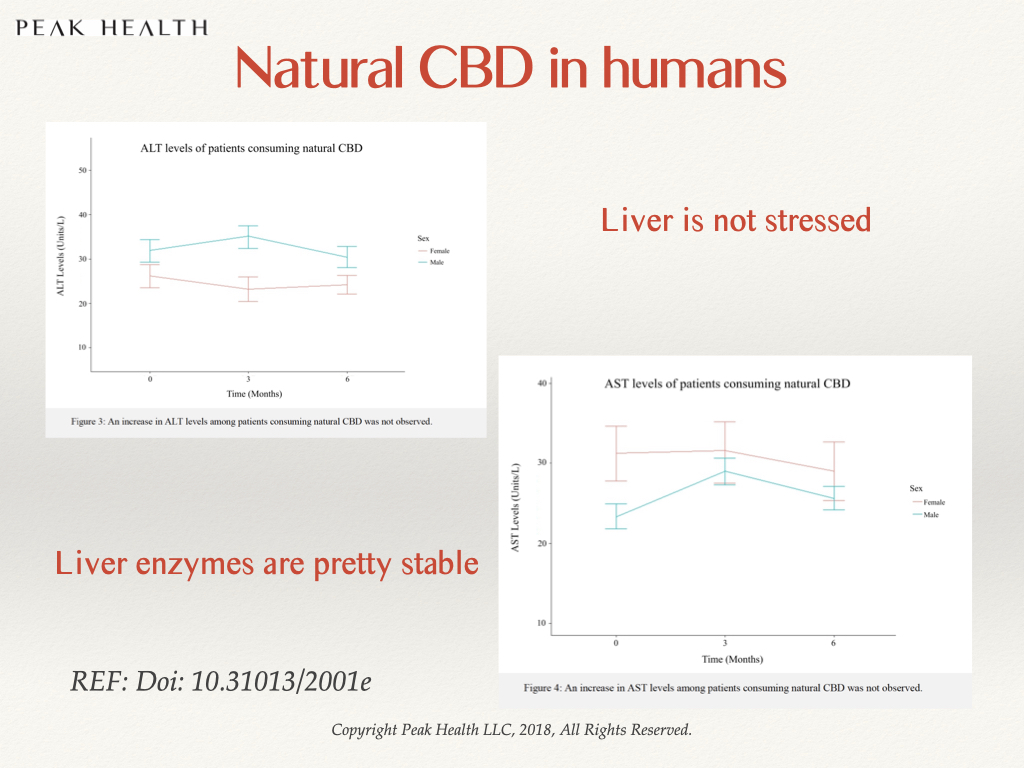
We published a study in 2018 showing that synthetic cannabinoids affected the liver by severely elevating ALT and AST levels. Natural CBD does not. Some students in India had acquired a supply of CBD that turned out to be hydrogenated CBD. They were monitored over time and advised to stop taking it. The hydrogenated CBD stressed out their liver, causing the ALT & AST liver enzymes to rise 10x beyond their baseline levels over a course of 10 weeks. The good news was that when they stopped taking it, their liver slowly recovered back to their baseline levels.
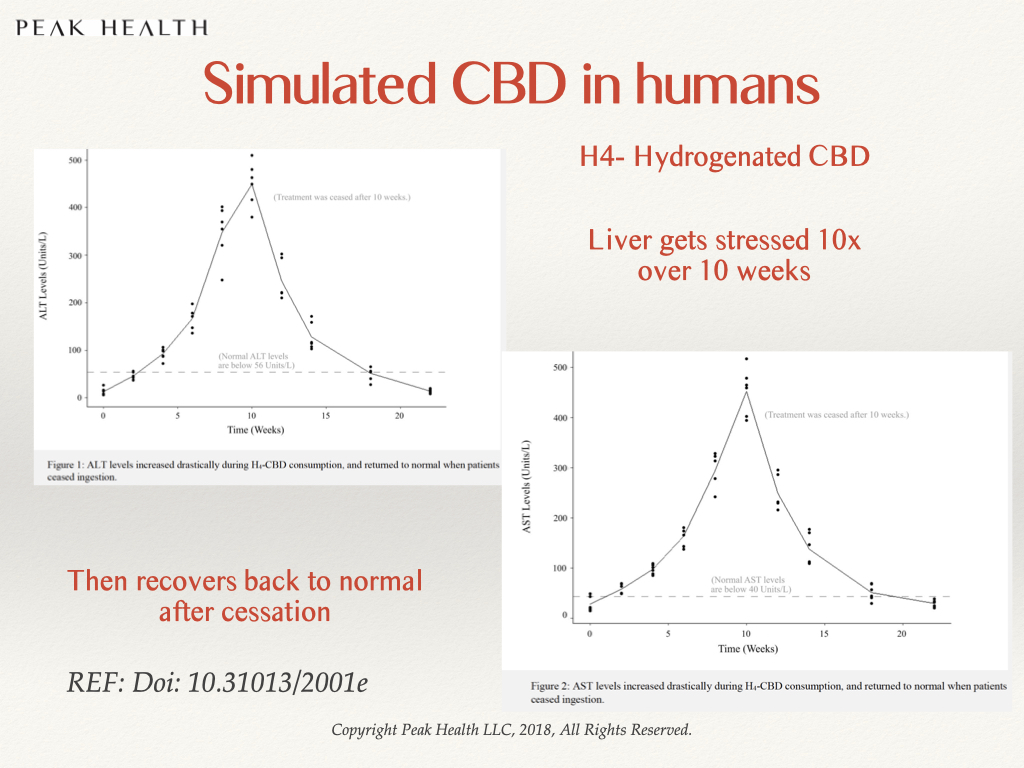
Synthetic THC analogues are well documented to be dangerous. When four patients were found “freaking out” and having a bad reaction to a synthetic cannabinoid (believed to be JWH-018), tests showed their liver enzyme levels to be highly elevated (more than 1000 units/L). Those who took synthetic (or “simulated”) CBD for 10 weeks averaged around 480 units/L and those who took botanical CBD averaged liver enzymes of only 40 units/L.
The only FDA-approved CBD, by prescription, is called Epidiolex. While it is claimed to be from a natural plant, it has a liver enzyme profile extremely similar to that of hydrogenated CBD. The FDA mandated a warning label that partly states “WARNING: Hepatocellular Injury: EPIDIOLEX can cause transaminase elevations.” Most of the people in the clinical trial for Epidiolex had a moderate-to-severe liver stress, which from our published data, is surprising.
Natural and Synthetic CBD Square Off
The big battle for the future of the pharmaceutical cannabinoids will be natural vs. synthetic cannabinoids.. The FDA-approved CBD is supposedly a natural extract but other pharmaceuticals want to go the synthetic route for stronger potency and more profits. There is an assumption that more potency is better and more likely to have therapeutic effects. Our prediction is that, in most cases, it is likely to cause a negative reaction.
Ensuring CBD Quality
There are more and more synthetic CBDs starting to show up on the markets, both listed and unlisted. The main tenets for the consumer to keep in mind are:
- Natural CBD provides a far more desired response in the human body than synthetic CBD.
- Flowers have higher bioactive molecules, like CBD, than leaves or stems. What smells more fragrant, a flower or the stalk?
- Vertically integrated vendors have more quality control over their products
- GC/MS and common lab tests measure quantity but not quality of CBD.
- Synthetic CBD scores very poorly on antibody bioactivity tests
- Natural CBD does not significantly elevate liver enzyme levels.
- Simulated (synthetic or denatured) CBD elevates liver enzymes levels but it can be reversed if discontinued.
All synthetic products are convenient to make. They are 100% pure (by definition), easy to make, easy to scale up and easy to mass produce. They are patentable and a pharmaceutical dream come true.
Manufacturing natural CBD is difficult and is a long process. Farming through production can be an industry that is highly fragmented. Farmers grow the plant. Aggregators buy the crops, aggregate them and sell them to oil/extract processors. Multiple vendors buy these oils. Some of this oil is converted to CBD isolate. All this happens before the final product is even made.
This is why we have kept the Kriya® Hops production a vertically integrated operation within the same organization. Constant innovation, scientific testing and learning has allowed for the applications of multiple patents and a uniquely qualified product. Peak Health, is to the CBD market, what Apple is, to the technology market.
Conclusion
Is it a far more tedious process to make natural CBD from Hops than synthetic CBD? Of course. There are many reasons why being in the business of peddling synthetic CBD is tantalizing. But there is only one reason we slog along, farm and laboriously process CBD from a plant— It is safer and healthier for you.

