Part 5– Nutritional Myth Series: Healthy Fats & Lipids: The Truth About Good and Bad Fats
🧠 Healthy Fats & Lipids: The Truth About Good and Bad Fats


Healthy fats and lipids are essential to your brain, hormones, and every cell membrane. This article explains the science of fats and how to use them to achieve Deep Health®.
This article explains the science of healthy fats and lipids, how they work inside you, and how to use them to achieve Deep Health®: physical, metabolic, and cardiovascular balance.

Fats (or lipids) are organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They provide twice as much energy as carbohydrates or proteins and are vital for:
Pro Tip
Healthy fats don’t make you fat — excess insulin and inflammation do.
Train your metabolism to burn fat as fuel by eating clean, moving daily, and sleeping deeply.

Structure: No double bonds; solid at room temperature.
Sources: Butter, ghee, coconut oil, cheese, red meat.
⚡ Important Point:
Choose shorter-chain saturated fats (like those in vegetable oil) over long-chain animal fats.


Cholesterol is not the villain it’s often made out to be—it’s a vital structural molecule that keeps every cell membrane stable, flexible, and functional. It also serves as the raw material for hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids that digest fats. The real issue arises when excess LDL cholesterol becomes oxidized and trapped in damaged arterial walls, sparking inflammation and plaque formation. Balanced nutrition, exercise, and stress control don’t “eliminate” cholesterol—they restore harmony between LDL and HDL, allowing this essential lipid to perform its life-sustaining work without turning harmful.

Trans fats are chemically altered vegetable oils made to mimic butter.
Your enzymes can’t recognize them because of the “twisted” bonds— and they cause:
⚡ Important Point:
Avoid anything labeled “partially hydrogenated oil.”
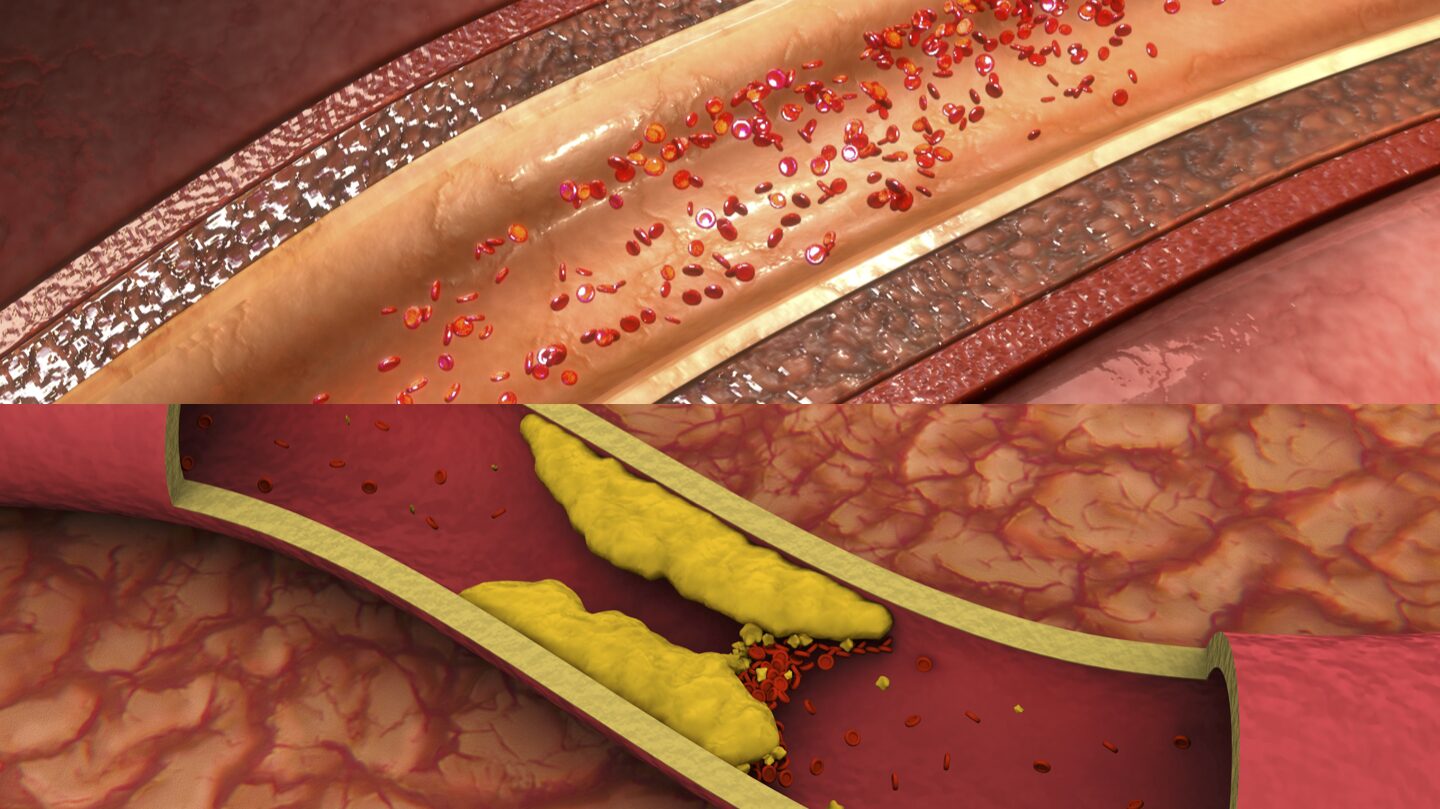
The Atherosclerosis Cycle
Cholesterol is essential — it:
The problem isn’t cholesterol itself, but oxidized LDL, which initiates inflammation inside artery walls.
Balancing Cholesterol Naturally
Phospholipids are special healthy fats and lipids that build every cell membrane and support brain and liver function.
Top Food Sources
Health Benefits
PS: Cooking Tip —
Use gentle cooking methods—high heat destroys delicate phospholipids. .
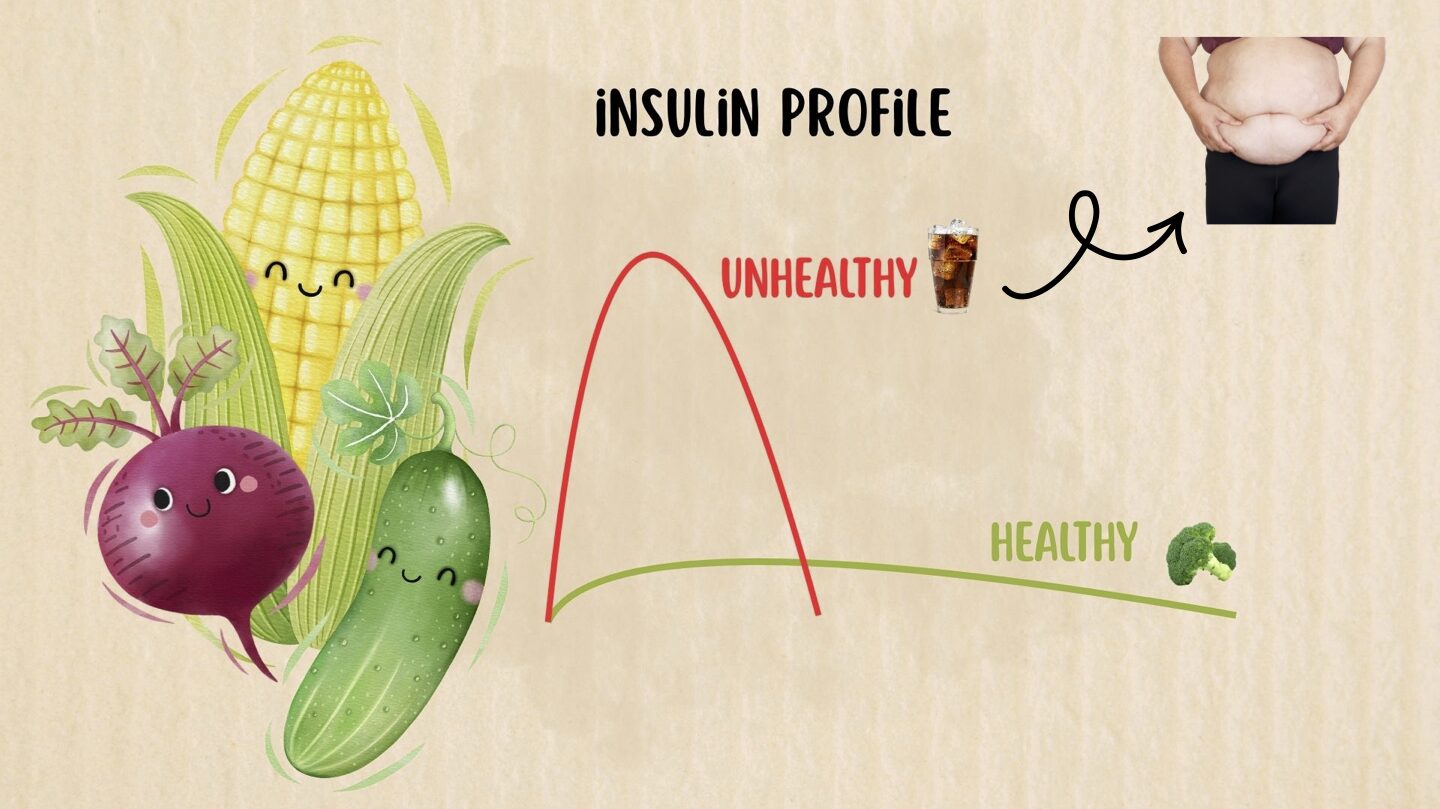
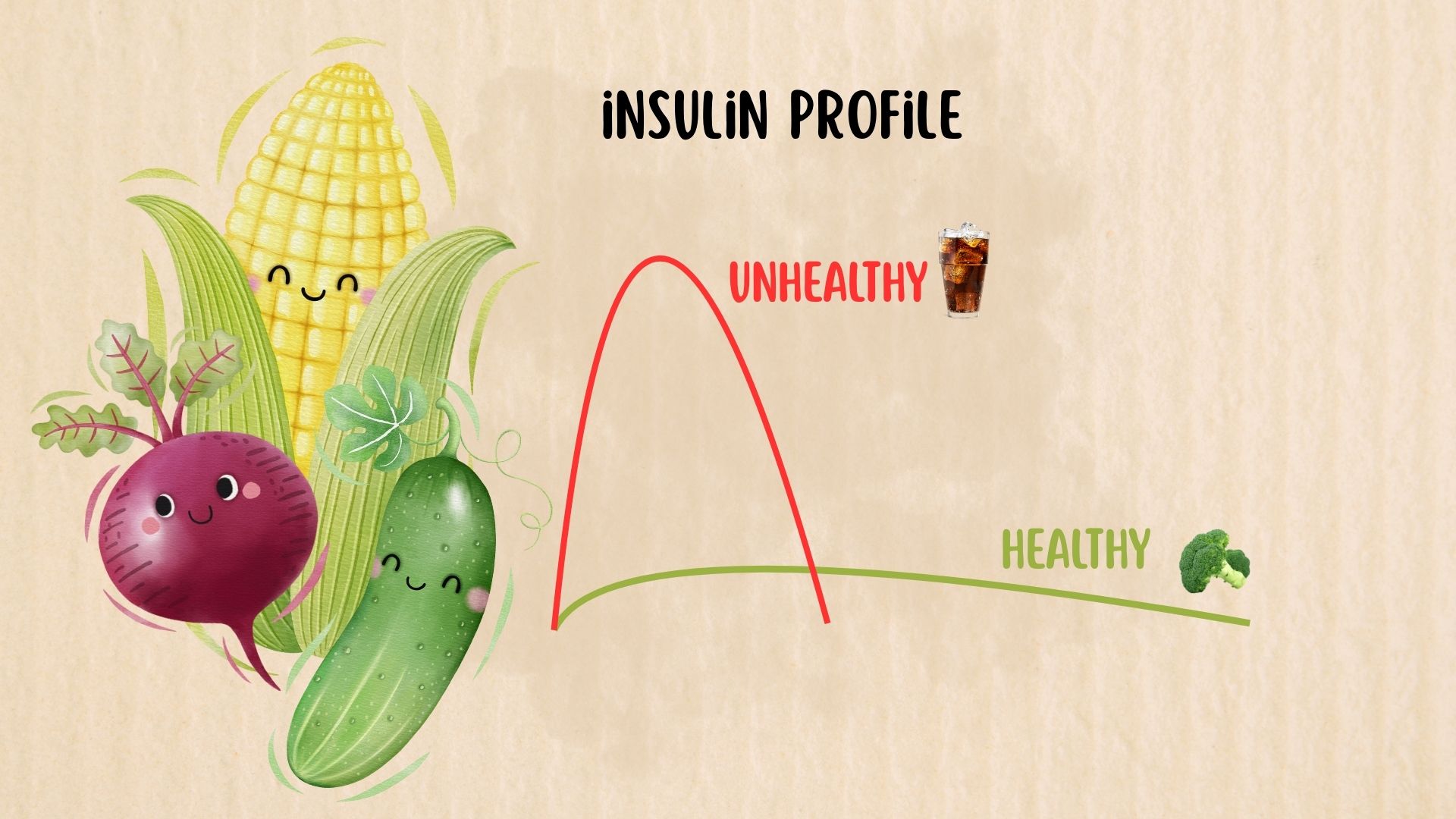
Your body can make fat even when you don’t eat it.
When insulin stays high due to excess carbohydrates, it triggers lipogenesis—the conversion of glucose into fat (triglycerides) for storage.
Triggers for Excess Fat Production
⚡ Important Point:
Control insulin by eating balanced meals, sleeping well, and training regularly.




Fat is not your enemy—it’s your body’s ally when balanced.
Use it wisely, choose it consciously, and understand it scientifically.
When your insulin, hormones, and healthy fats and lipids are in harmony, your body becomes efficient, lean, and resilient.
"Health is balance. Fat is energy. Discipline is medicine.”
Dr. Bomi Joseph Tweet
1. Fat Is Essential — Not Evil
Fats fuel your brain, hormones, and cells. The goal isn’t zero fat — it’s the right kind of fat in the right balance.
2. Choose Natural, Not Processed
Use olive oil, avocados, coconut oil, nuts, and fatty fish.
Avoid trans fats and seed oils that trigger inflammation and oxidative stress.
3. Balance Omega-3 and Omega-6
Modern diets overload on Omega-6 (soy, corn, canola).
Increase Omega-3 intake (salmon, flax, walnuts) for better heart and brain health.
4. Control Insulin to Burn Fat
Excess carbs spike insulin, which stores fat.
Steady energy and fat loss come from stable insulin levels — achieved through mindful eating, fasting, and exercise.
5. Protect Your Heart, Reverse Plaque
You can reverse early atherosclerosis by:
• Eliminating trans fats
• Eating fiber and antioxidants
• Managing stress and staying active daily
World Health Organization. Trans fat (Fact sheet, updated 2024). Replacing industrial trans fats lowers CVD risk; recommended intake <1% of energy. World Health Organization
World Health Organization. WHO plan to eliminate industrially-produced trans-fatty acids from the global food supply (2018). Diets high in trans fat ↑ heart disease risk by ~21%; mortality ↑ ~28%. World Health Organization
American Heart Association. What is Atherosclerosis? (2024 overview of plaque formation and narrowing). www.heart.org
Hong CG, et al. Oxidized LDL associates with atherosclerotic plaque progression. 2023 review of oxLDL, macrophage activation, and VSMC effects. PMC
Holvoet P, et al. Oxidized LDLs are rapidly taken up by macrophages to form foam cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. (classic mechanistic paper). American Heart Association Journals
Liu X, et al. Regulation of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the immune system. Front Immunol. 2023. (GPR41/43/109A; immune effects). PMC
Facchin S, et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Human Health. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. (SCFA receptors and systemic benefits). PMC
Xu J, et al. SCFA receptors and blood pressure/host signaling (GPR41/43/109A). 2022 review. PMC
Skulas-Ray AC, et al. Omega-3 Fatty Acids for the Management of Hypertriglyceridemia (AHA Science Advisory). Circulation. 2019. (4 g/day lowers TG ≥30% in very high TG). American Heart Association Journals+1
Soliman GA. Dietary Fiber, Atherosclerosis, and CVD. Nutrients. 2019. (soluble fiber lowers LDL via multiple mechanisms). PMC
Ghavami A, et al. Soluble Fiber Supplementation and Serum Lipid Profile. Front Nutr. 2023. (dose-response reductions in TC and LDL). PMC
AHA. Trans fats (policy & status; U.S. PHO phase-out; why they were used). 2025 update. www.heart.org
NCBI InformedHealth. What is cholesterol and how does arteriosclerosis develop? (2025 patient-friendly overview; oxidized LDL concept). NCBI
Dhaka V, et al. Trans fats—sources, health risks, alternatives. (mechanisms; insulin resistance).